Using Amazon RDS with MySQL
This guide describes how to deploy a MySQL database using Amazon RDS.
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)
Amazon RDS is a managed service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the AWS Cloud. It provides cost-efficient, resizable capacity for an industry-standard relational database and manages common database administration tasks. It has support for several engines such as Amazon Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, and SQL Server.
Deploy Amazon RDS MySQL
To deploy a MySQL database using Amazon RDS, you first need to retrieve some configuration parameters.
If you created your EKS cluster using eksctl, use the following commands to find your VpcId, SubnetId, and SecurityGroupId. For clusters created in other ways, be sure to find these values before deploying your database.
export AWS_CLUSTER_NAME=<your_cluster_name>
# Retrieve your VpcId.
aws ec2 describe-vpcs \
--output json \
--filters Name=tag:alpha.eksctl.io/cluster-name,Values=$AWS_CLUSTER_NAME \
| jq -r '.Vpcs[].VpcId'
# Retrieve the list of SubnetIds for your cluster's Private subnets. Select at least 2.
aws ec2 describe-subnets \
--output json \
--filters Name=tag:alpha.eksctl.io/cluster-name,Values=$AWS_CLUSTER_NAME Name=tag:aws:cloudformation:logical-id,Values=SubnetPrivate* \
| jq -r '.Subnets[].SubnetId'
# Retrieve the SecurityGroupId for your nodes.
# Note: This assumes that your nodes share the same SecurityGroup
INSTANCE_IDS=$(aws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].InstanceId' --filters "Name=tag-key,Values=eks:cluster-name" "Name=tag-value,Values=$AWS_CLUSTER_NAME" --output text)
for i in "${INSTANCE_IDS[@]}"
do
echo "SecurityGroup for EC2 instance $i ..."
aws ec2 describe-instances --output json --instance-ids $i | jq -r '.Reservations[].Instances[].SecurityGroups[].GroupId'
done
With this information in hand, you can now use either the Amazon RDS console or the attached CloudFormation template to deploy your database.
Warning
The CloudFormation template deploys Amazon RDS for MySQL that is intended for a Dev/Test environment. We highly recommend deploying a Multi-AZ database for Production use. Please review the Amazon RDS documentation to learn more.Select your desired Region in the AWS CloudFormation management console then click Next.
We recommend that you change the DBPassword. If you do not, the password will default to Kubefl0w. Select your VpcId, Subnets, and SecurityGroupId, then click Next.
For the remaining options, choose the default settings by clicking Next. Then click Create Stack.
Once the CloudFormation stack creation is complete, click on Outputs to get the RDS endpoint.
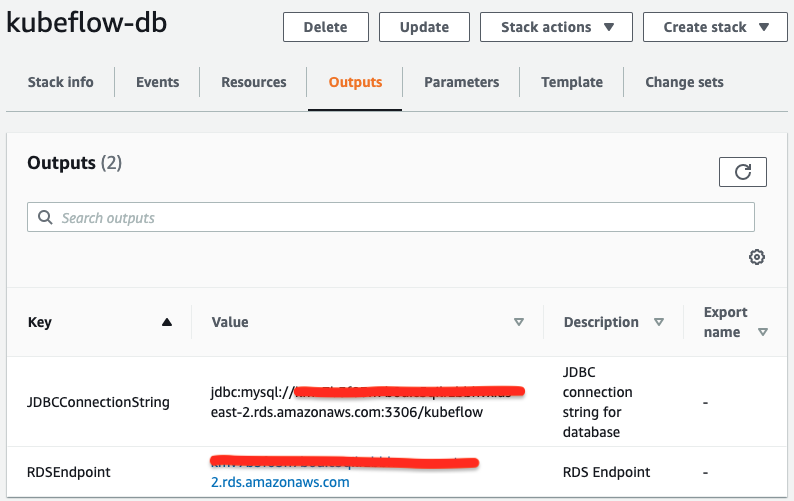
If you did not use CloudFormation, you can retrieve the RDS endpoint through the RDS console on the Connectivity & Security tab in the Endpoint & Port section.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.
